Education



Experience





I am an AR/VR Research Scientist in Global Technology Applied Research at JPMorganChase, where I design and study XR systems that support human collaboration in complex, real-world settings. My research sits at the intersection of XR, HCI/CSCW, and AI-enabled interaction, focusing on how spatial interfaces can enhance shared awareness, decision making, and group work.
I build XR + AI systems that integrate spatial interaction with perception, multimodal language models, and agent-based workflows. Rather than treating AI as a standalone assistant, my work explores how AI can operate within XR environments to surface relevant context, enable parallel work, and maintain traceability across collaborative activities.
My work has explored collaborative meetings, hybrid events, mentoring, and collaborative decision-making, and has been published in venues such as ACM CHI, CSCW, and IEEE ISMAR.
I received my PhD in Information Science from Cornell University, following BS/MS degrees in Computer Science.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Research Highlights

S-TIER: Situated-Traceable Insights in Extended Reality for Hybrid Crisis Management
Cheng-Yao Wang, et al.
Under review
We present S-TIER, a framework and prototype that convert crisis-team conversation and multimodal context into situated, traceable XR insights to support hybrid and asynchronous response work.
Crisis response teams collaborate in hybrid settings, coordinating under time pressure. Remote participants often lack access to wall displays that anchor situational awareness, leading to fragmented context and uneven participation. These challenges are compounded by asynchronous workflows, where team representatives join mid-session and rely on overviews to catch up. We investigate these gaps through a multi-stage study with crisis management experts. From formative interviews and an exploratory hybrid XR prototype, we distilled design goals around shared context, overview preparation, and traceability. We then propose the \framework{} framework, which transforms conversations into situated and traceable insights that retain links to their original sources. A proof-of-concept prototype realizes this framework by combining multimodal context capture, structured insight extraction, and situated visualization, evaluated in simulated crisis scenarios with two remote response teams. Findings highlight design considerations for asynchronous participation, adaptive summarization, and traceability, advancing pathways toward real-world deployment of hybrid XR crisis systems.
# XR # LLM/VLM # Collaboration # Human-Agent-Interaction
S-TIER: Situated-Traceable Insights in Extended Reality for Hybrid Crisis Management
Cheng-Yao Wang, et al.
Under review
TL;DR: We present S-TIER, a framework and prototype that convert crisis-team conversation and multimodal context into situated, traceable XR insights to support hybrid and asynchronous response work.
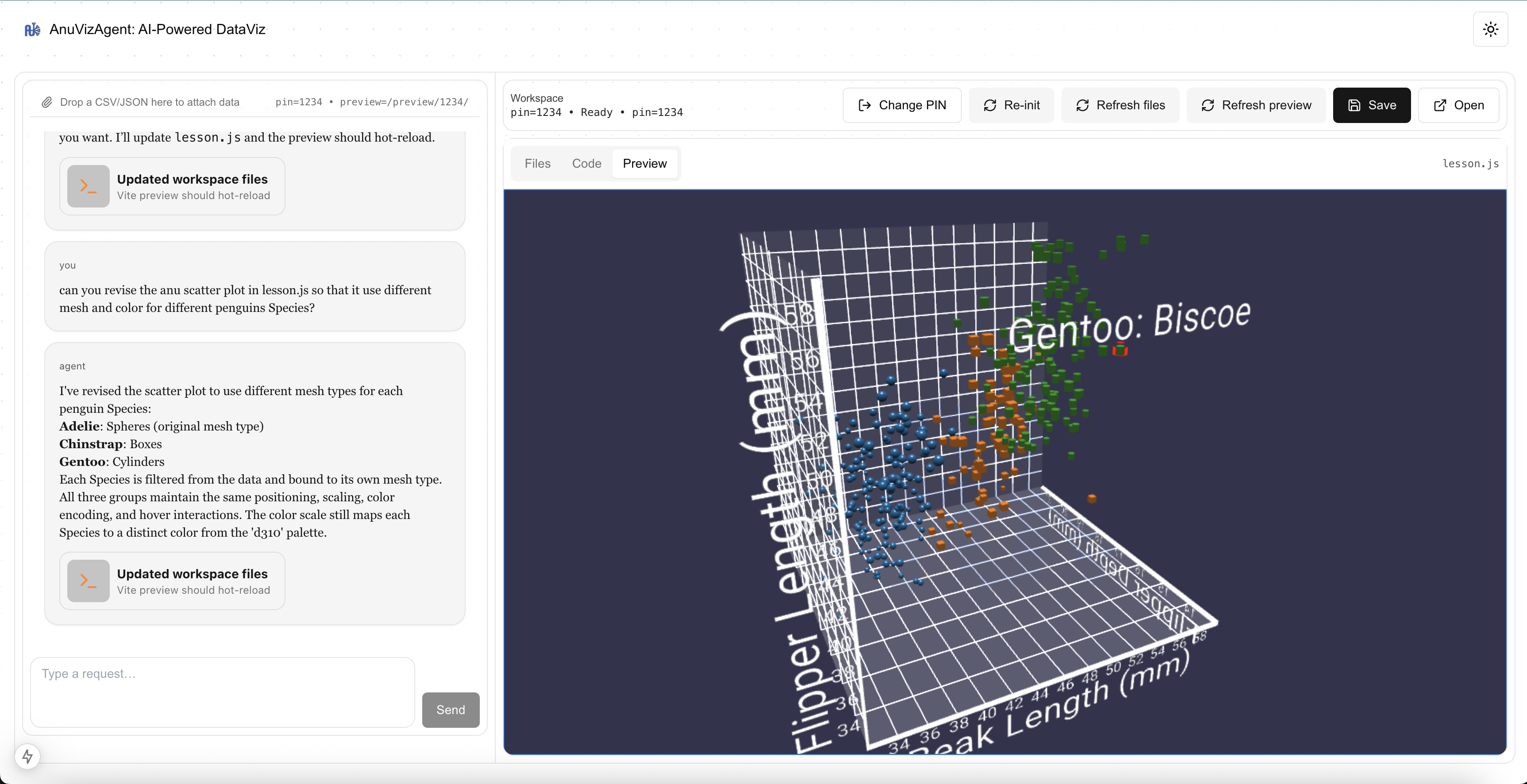
AnuVizAgent: A Live AI-Driven Workflow for Immersive Visualization
Cheng-Yao Wang
Ongoing Research Project
AnuVizAgent enables users to transform raw data into immersive WebXR visualizations through natural language interaction, with AI agents generating live, executable visualization code.
Creating immersive visualizations typically requires significant expertise in graphics, web development, and XR frameworks, posing a high barrier for exploratory data analysis. This project explores an interactive workflow that enables users to transform raw datasets into immersive, web-based visualizations through natural language interaction. Users begin by uploading structured data (e.g., CSV or JSON) and iteratively describing desired visual outcomes in a chat interface. An AI agent translates these high-level intents into executable Anu.js and Babylon.js code, which is injected into a live Vite development server and rendered in real time with hot reloading. Crucially, the same visualization is accessible across devices: users can refine results on a desktop browser and seamlessly view the identical, continuously updated scene in a WebXR-enabled headset such as Apple Vision Pro via a shared HTTPS endpoint. By combining AI-assisted code generation, live web visualization, and device-agnostic delivery, AnuVizAgent lowers the barrier to creating and exploring immersive data representations.
# XR LLM/VLM # Human-Agent Interaction
AnuVizAgent: A Live AI-Driven Workflow for Immersive Visualization
Cheng-Yao Wang
Ongoing Research Project
TL;DR: AnuVizAgent enables users to transform raw data into immersive WebXR visualizations through natural language interaction, with AI agents generating live, executable visualization code.
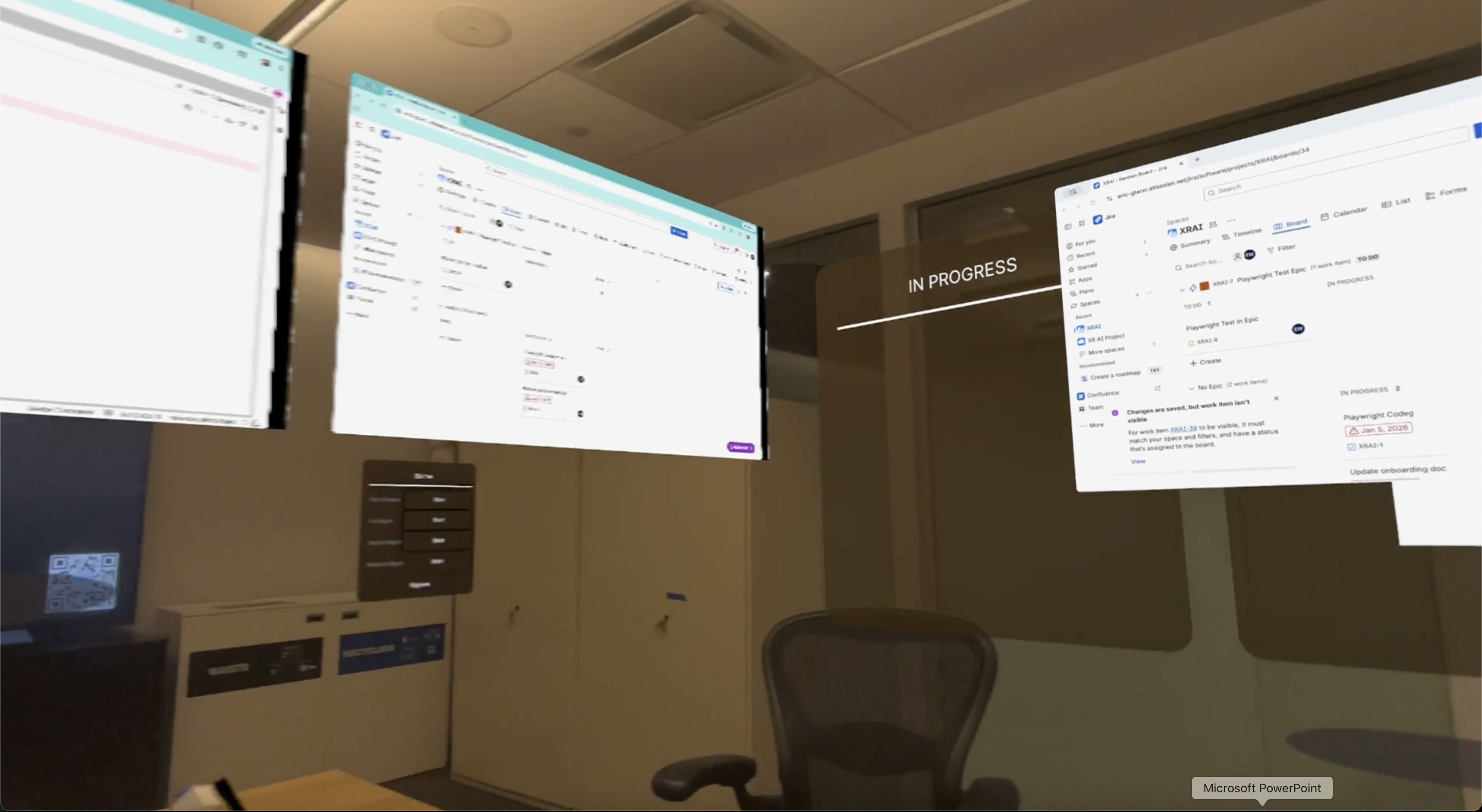
From Discussion to Action: Delegated Work in XR Team Meetings
Cheng-Yao Wang
Ongoing Research Project
This project explores how XR meetings can support delegated work during the meeting itself, enabling agents to carry out bounded tasks in parallel without disrupting group interaction.
Team meetings often involve identifying actionable tasks but require participants to defer execution until after the meeting or to multitask in ways that fragment attention and collaboration. This project investigates how Extended Reality (XR) team meetings can support delegated work during the meeting itself, without requiring participants to step out of the shared interaction. We explore a new interaction paradigm in which shared windows in XR meetings are augmented with agent capabilities that can carry out bounded tasks in parallel under human oversight. Leveraging XR-specific affordances—such as spatial organization, visibility, and non-verbal cues—we study how agents can identify actionable intent, request input in minimally disruptive ways, and make execution progress visible to the group. Through system design and empirical studies, this work examines how in-meeting delegation reshapes collaboration dynamics, feedback loops, and meeting practices, informing the design of future XR-based collaborative workspaces.
# XR # Collaboration # Agents # LLM/VLM # Human-Agent-Interaction
From Discussion to Action: Delegated Work in XR Team Meetings
Cheng-Yao Wang
Ongoing Research Project
TL;DR: This project explores how XR meetings can support delegated work during the meeting itself, enabling agents to carry out bounded tasks in parallel without disrupting group interaction.
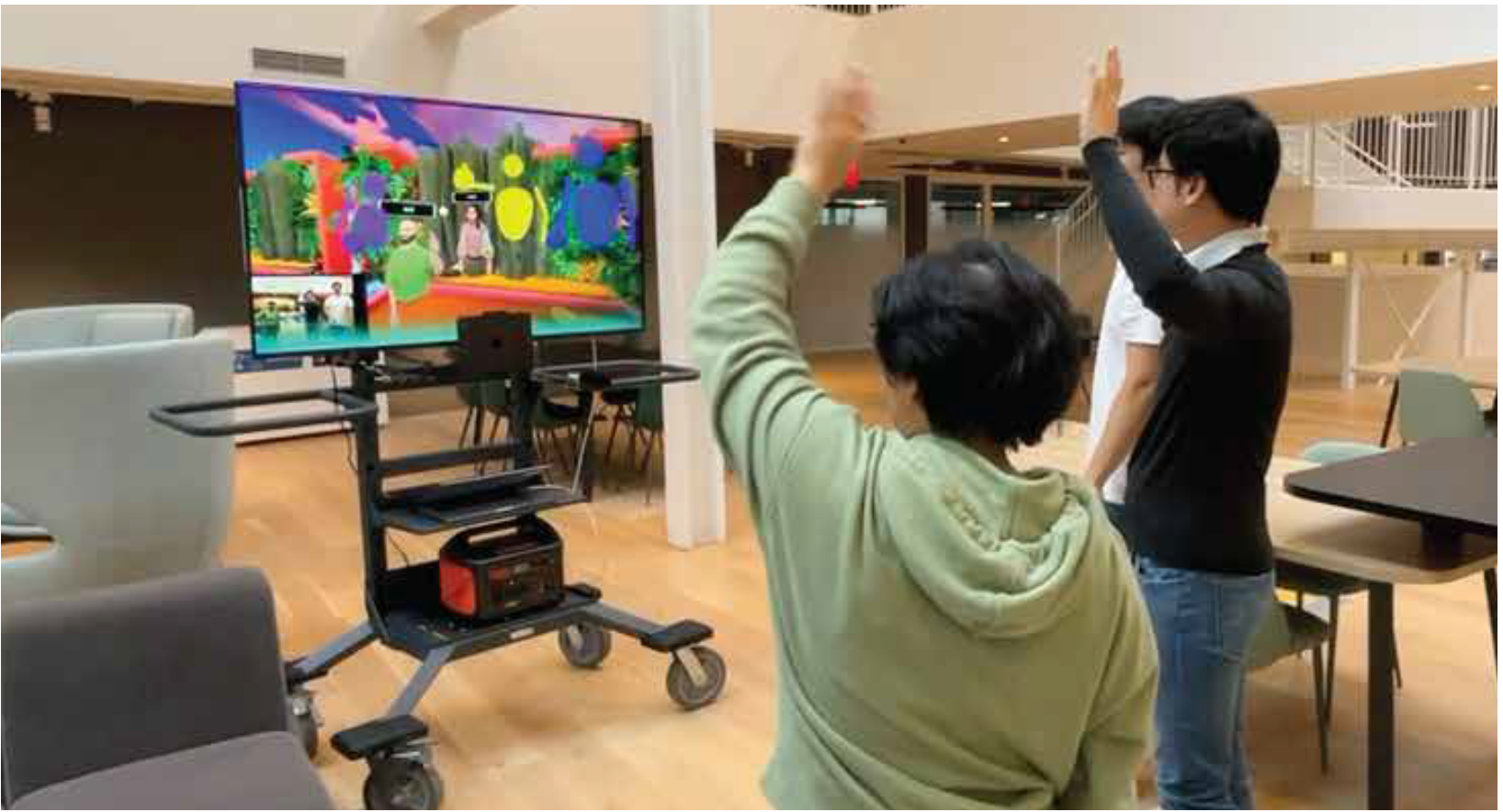

HybridPortal: Enabling Hybrid Group Interactions in Hybrid Events
Cheng-Yao Wang, et al.
Under review
HybridPortal introduces a mobile, portal-based system that bridges physical and virtual event spaces, enabling shared group interactions and social engagement between in-person and remote attendees.
Hybrid events are increasingly prevalent, offering in-person and remote participation to enhance inclusivity and sustainability. However, they often fail to create cohesive experiences, leaving remote participants feeling disconnected from in-person interactions. We present HybridPortal, a novel system that transforms a large monitor into a movable portal, bridging virtual and physical event spaces. By streaming AR video from the physical venue, HybridPortal allows remote attendees to interact with in-person attendees and view the surrounding physical environment as in-person attendees move the portal through the venue, while in-person attendees navigate and engage with remote attendees in the virtual space. We deployed HybridPortal at a hybrid conference, implementing hybrid group activities to explore its impact on social interactions. Our findings demonstrate how HybridPortal’s mobility and cross-realm interactions enhance social presence, facilitate group engagement, and inform the design of future hybrid systems. We contribute insights into leveraging spatial dynamics and hybrid group interactions to create more cohesive and engaging social experiences for hybrid events.
# XR # Computer Vision # Collaboration
HybridPortal: Enabling Hybrid Group Interactions in Hybrid Events
Cheng-Yao Wang, et al.
Under review
TL;DR: HybridPortal introduces a mobile, portal-based system that bridges physical and virtual event spaces, enabling shared group interactions and social engagement between in-person and remote attendees.
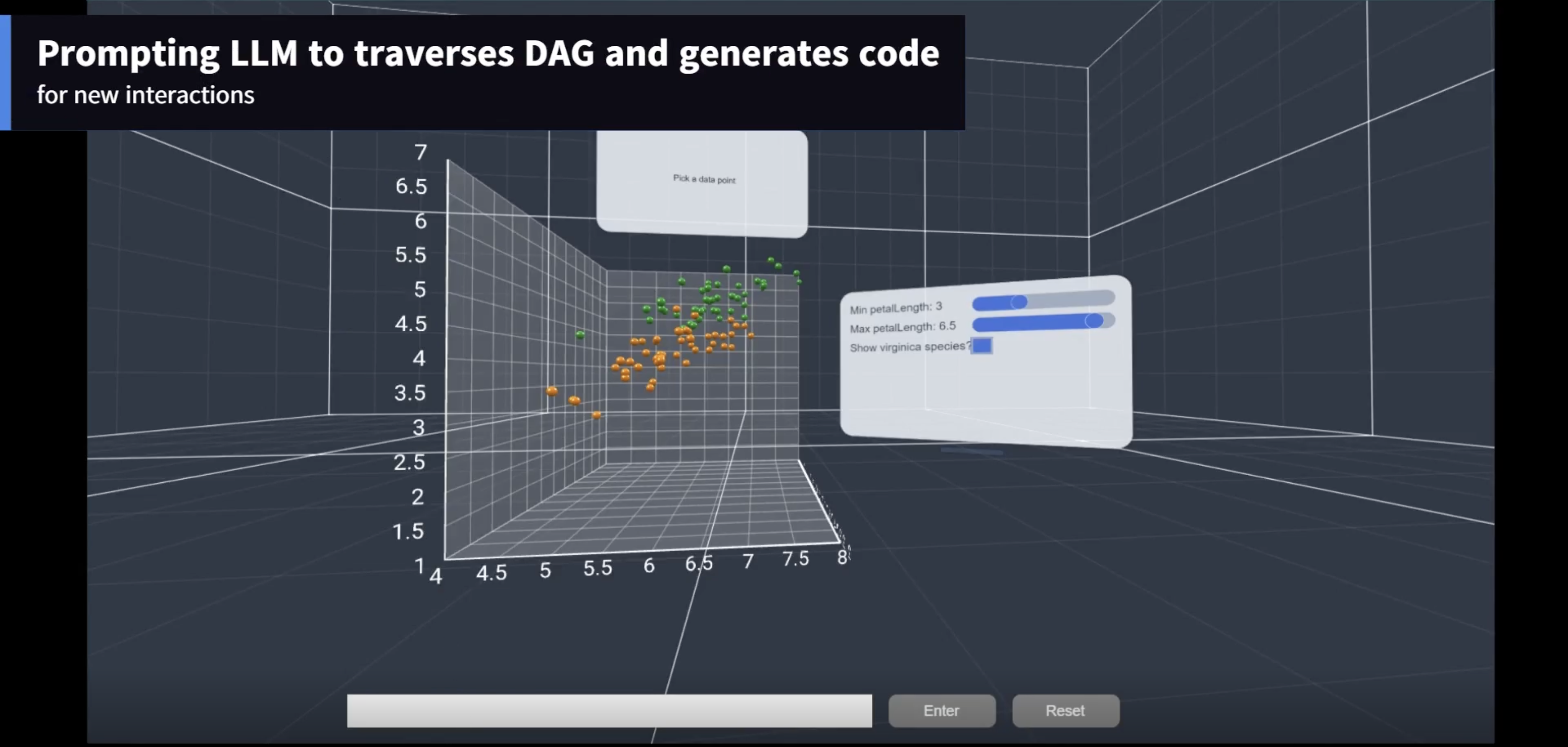
XRCopilot: A Lightweight and Generalizable Approach for Conversational Interaction in XR
Cheng-Yao Wang
Research Prototype
XRCopilot enables conversational interaction in XR by automatically exposing application logic and interaction context to language models through a lightweight, code-driven approach.
We present XRCopilot, a lightweight and generalizable approach for enabling conversational interaction in Extended Reality (XR) environments, including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). Instead of relying on application-specific instrumentation or handcrafted interaction schemas, XRCopilot leverages a TypeScript transformer built on the TypeScript Compiler API to automatically extract function comments, source code, and call stacks during user interactions in XR applications. These signals are continuously organized into a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) that captures the structure of user interactions at runtime. Each node in the DAG represents a function invocation together with its semantic and implementation context, allowing language models to reason about user actions, system state, and interaction history. By grounding conversational agents directly in application execution, XRCopilot provides a scalable foundation for building XR conversational interfaces that are transparent, adaptable, and reusable across XR systems.
# XR # LLM/VLM
XRCopilot: A Lightweight and Generalizable Approach for Conversational Interaction in XR
Cheng-Yao Wang
Research Prototype
TL;DR: XRCopilot enables conversational interaction in XR by automatically exposing application logic and interaction context to language models through a lightweight, code-driven approach.
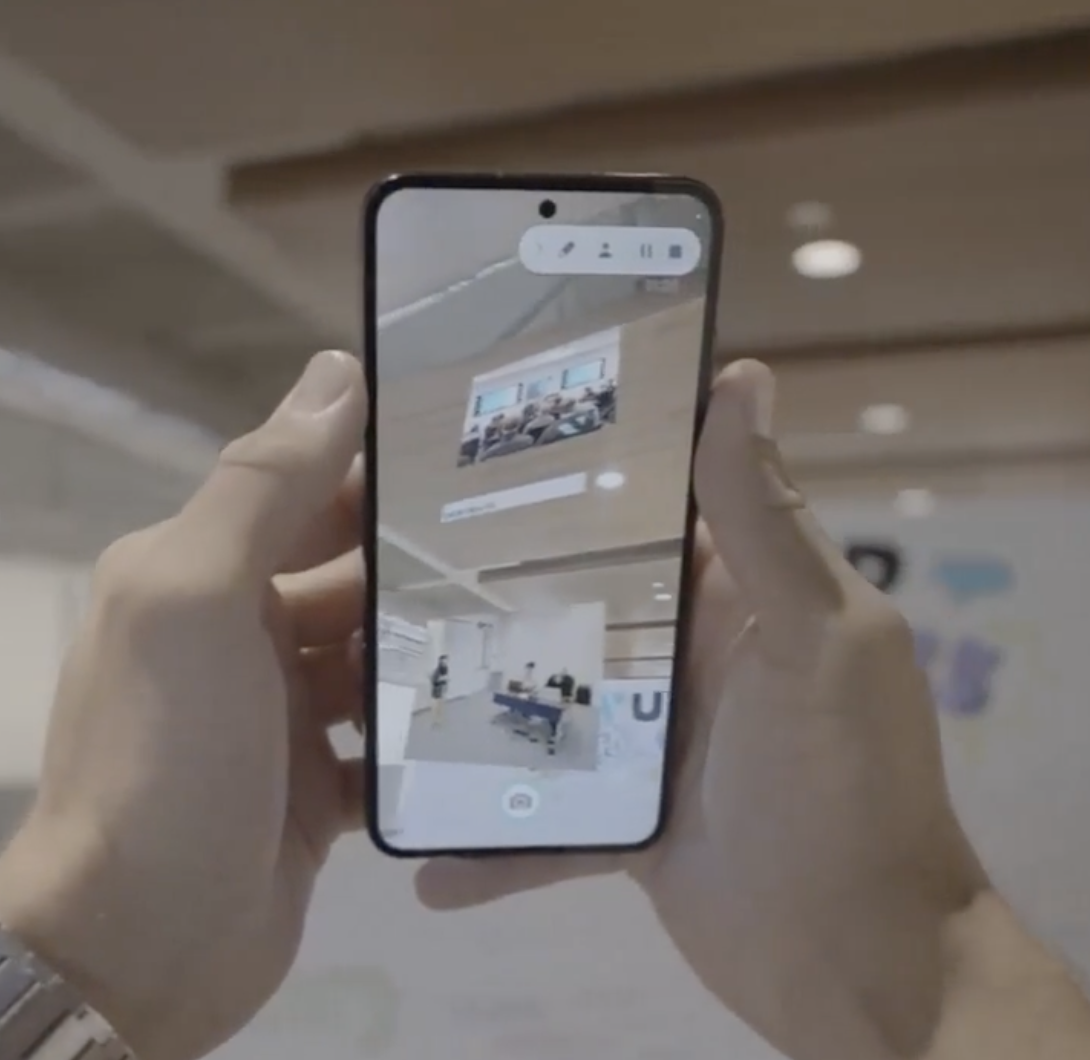

SocialMiXR: Facilitating Hybrid Social Interactions at Conferences
Cheng-Yao Wang*, Fannie Liu*, William Moriarty, Feiyu Lu, Usman Mir, David Saffo, Mengyu Chen, Blair MacIntyre
PACM HCI (CSCW 2025)
SocialMiXR demonstrates how aligning physical and virtual spaces using WebXR can enable shared social activities and foster meaningful interaction between in-person and remote conference attendees.
[Abstract] [DOI] [Paper] [Video]
Hybrid options at conferences, which support in-person and remote attendance, have increasingly become the norm in order to broaden participation and promote sustainability. However, hybrid conferences are challenging, where in-person and remote attendees often have disjoint, parallel experiences with limited opportunity to interact with each other. To explore the potential for facilitating social interaction between in-person and remote conference attendees, we designed and built SocialMiXR, a research prototype that uses WebXR technologies to align the physical and virtual worlds into one hybrid space for socialization. We deployed SocialMiXR in a three-day field study with 14 in-person and remote attendees of an engineering conference. Our qualitative results demonstrate that participants felt they were together in the same conference experience and formed meaningful connections with each other. At the same time, they faced difficulties balancing different realities and capabilities given their separate contexts. We discuss implications for the design of hybrid social experiences at conferences.
# XR # Collaboration
SocialMiXR: Facilitating Hybrid Social Interactions at Conferences
Cheng-Yao Wang*, Fannie Liu*, William Moriarty, Feiyu Lu, Usman Mir, David Saffo, Mengyu Chen, Blair MacIntyre
PACM HCI (CSCW 2025)
TL;DR: SocialMiXR demonstrates how aligning physical and virtual spaces using WebXR can enable shared social activities and foster meaningful interaction between in-person and remote conference attendees.
AvatarPilot: Decoupling One-to-One Motions from Their Semantics with Weighted Interpolations
Cheng-Yao Wang, Eyal Ofek, Hyunju Kim, Payod Panda, Andrea Stevenson Won, Mar Gonzalez-Franco
ISMAR Adjunct 2024
AvatarPilot decouples raw avatar motion from semantic intent, enabling flexible transformation of pointing, gaze, and locomotion behaviors across physically constrained mixed reality spaces.
[Abstract] [Abstract] [DOI] [Paper] [Video]
Physical restrictions of the real spaces where users are situated present challenges to remote XR and spatial computing interactions using avatars. Users may not have sufficient space in their physical environment to duplicate the physical setup of their collaborators. However, when avatars are relocated to accommodate space constraints, one-to-one motions may no longer preserve their intended meaning. We propose AvatarPilot, a system that uses weighted interpolations to decouple low-level avatar motion from higher-level semantic intent. This approach ensures that collaborators look at and point to the same objects locally and remotely, while preserving non-object-directed gestures and postures near the body. We extend this technique to support locomotion and direct interactions in near space, such as grabbing objects, enabling more flexible use of inverse kinematics (IK). We discuss applications and limitations of this approach and release AvatarPilot as an open-source toolkit to support future mixed reality collaboration systems.
# XR # Collaboration
AvatarPilot: Decoupling One-to-One Motions from Their Semantics with Weighted Interpolations
Cheng-Yao Wang, Eyal Ofek, Hyunju Kim, Payod Panda, Andrea Stevenson Won, Mar Gonzalez-Franco
ISMAR Adjunct 2024
TL;DR: AvatarPilot decouples raw avatar motion from semantic intent, enabling flexible transformation of pointing, gaze, and locomotion behaviors across physically constrained mixed reality spaces.
